

Examples of hinge joints include the elbow, knee, ankle, and joints between the bones of the fingers and toes. Similar to a door hinge, movement is limited to a single direction.
Hinge Joint: This joint permits bending and straightening movements along one plane. It allows the head to turn from side to side. The joint between the first and second cervical vertebrae near the base of the skull is an example of a pivot joint. The bone that pivots may either rotate within the ring or the ring may rotate around the bone. One bone is encircled by a ring formed by the other bone at the joint and a ligament. Pivot Joint: This joint permits rotational movement around a single axis. This specialized joint is also called a peg and socket joint and allows for limited to no movement. A gomphosis is an exception to the rule that joints connect bone to bone, as it connects teeth to bone. Gomphosis: This type of fibrous joint holds a tooth in place in its socket in the upper and lower jaw. A syndesmosis can be found between the bones of the forearm (ulna and radius) and between the two long bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula). The bones are linked by ligaments or a thick membrane (interosseous membrane). Syndesmosis: This type of fibrous joint connects two bones that are relatively far apart. Overtime, cranial bones fuse together providing more stability and protection for the brain. In newborns and infants, bones at these joints are separated by a larger area of connective tissue and are more flexible. In adults, the bones are held tightly together to protect the brain and help shape the face. Sutures: These narrow fibrous joints connect bones of the skull (excluding the jaw bone). Occipital fontanelle – It is located at the junction of the lambdoid sutures and sagittal. Frontal fontanelle – It is located at the junction of the sagittal sutures and coronal. Lambdoid suture – Lambdoid suture fuses the occipital bone to the two parietal bones.įontanelles are membrane spaces between the bones that form in newborns due to incompletely fused suture joints. Sagittal suture - Sagittal Suture fuses both parietal bones to each other. Coronal suture- Coronal Suture fuses the frontal bone with the two parietal bones. These joints represent points of potential weakness in the skull and are important in the context of trauma.īelow mentioned are the main sutures in the adult skull are: Sutures are a form of immovable fibrous joint found only in the skull, and they also fuse entirely at the age of 20. The upper teeth are rooted in the two maxillae while the lower teeth are rooted in the mandible and the maxillae also contain paranasal sinuses like the ethmoid, frontal and sphenoid bones of the cranium.īelow mentioned is the list of bones in the ear. 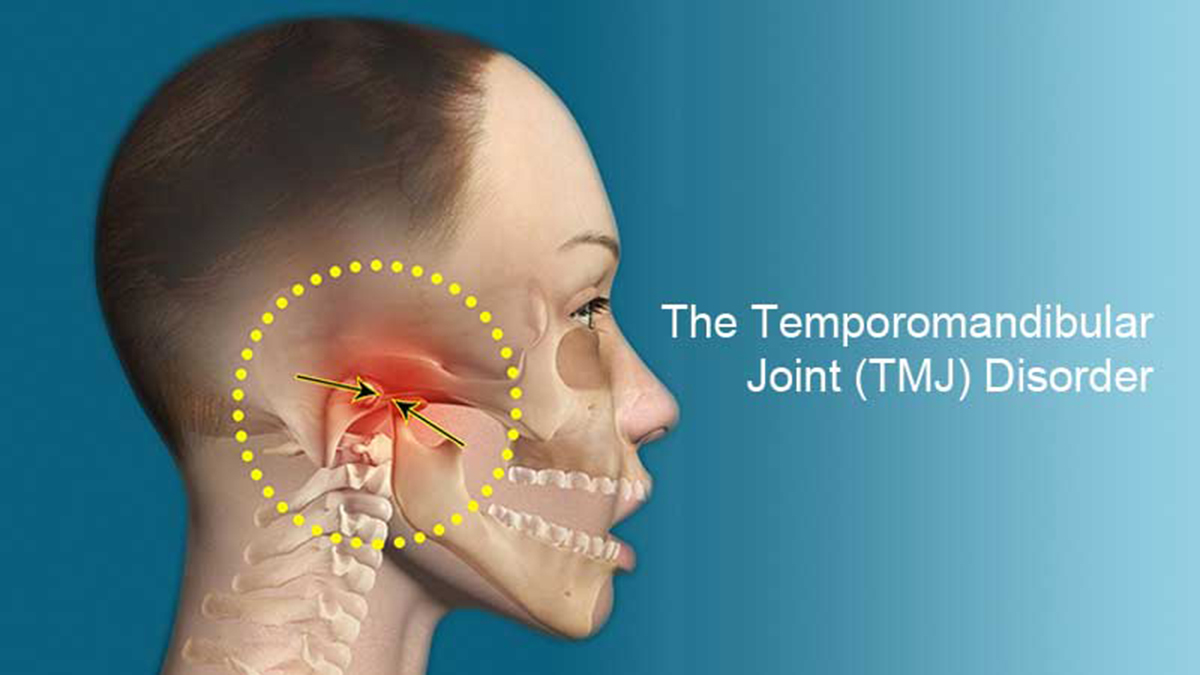
The mandible, or jaw bone, is the only movable bone of the skull and it forms the temporomandibular joint with the temporal bone. Mandible (jaw) – It articulates with the base of the cranium at the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).Vomer – Vomer forms the posterior aspect of the nasal septum.Maxilla (2) – It comprises part of the upper jaw and hard palate.Palatine (2) – It is situated at the rear of the oral cavity and forms part of the hard palate.Inferior nasal conchae (2) – Inferior nasal conchae are located within the nasal cavity, these bones increase the surface area of the nasal cavity and thus they help in increasing the amount of air that comes into contact with the cavity walls.

Nasal (2) – These are the two slender bones that are located at the bridge of the nose.Lacrimal (2) – It is the smallest bones of the face which form part of the medial wall of the orbit.Zygomatic (2) – Zygomatic is a bone that forms the cheekbones of the face and articulates with the frontal, sphenoid, temporal, and maxilla bones.The frontal bone is sometimes included as part of the facial skeleton and is typically a bone of the calvaria. The orbits of the eyes, the nasal and oral cavities, and the sinuses are all fused together by 14 bones. The facial skeleton is also known as the viscerocranium which supports the soft tissues of the face.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
